Ikaria introduces the INOMAX NICU PRO App. This app was designed to provide healthcare professionals a set of NICU related calculators to assist with the most commonly used calculations.
The NICU PRO contains five calculators:
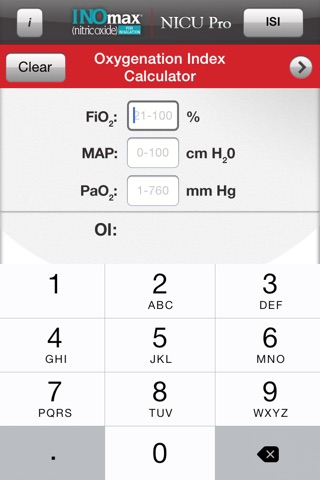
Oxygenation Index Calculator
AaDO2 Calculator
Pregnancy/Gestational Age Calculator
Fractional Excretion of Sodium (FENa) Calculator
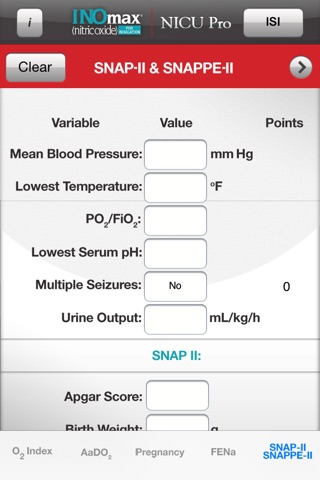
SNAP-II & SNAPPE-II
Download the free INOMAX NICU PRO App now and obtain a useful tool.
INOMAX® is a vasodilator, which, in conjunction with ventilatory support and other appropriate agents, is indicated for the treatment of term and near-term (>34 weeks gestation) neonates with hypoxic respiratory failure associated with clinical or echocardiographic evidence of pulmonary hypertension, where it improves oxygenation and reduces the need for extracorporeal membrane oxygenation.
INOMAX Important Safety Information
INOMAX should not be used in the treatment of neonates known to be dependent on right-to-left shunting of blood
Methemoglobinemia is a dose-dependent side effect of inhaled nitric oxide therapy. Therefore, methemoglobin levels should be monitored during INOMAX administration. Caution should be used when administering INOMAX with other drugs that can cause methemoglobinemia regardless of their route of administration
Nitrogen dioxide (NO2) rapidly forms in gas mixtures containing nitric oxide and oxygen. NO2 formed in this way can cause airway inflammation and damage
INOMAX must be administered through a system that does not cause excessive generation of NO2 and that monitors for NO, NO2, and FiO2
Abrupt discontinuation of INOMAX therapy can lead to worsening of PaO2 and increasing pulmonary artery pressure (PAP). Deterioration in oxygenation and elevation in PAP can also occur in children with no apparent response to INOMAX
In patients with pre-existing left ventricular dysfunction, inhaled nitric oxide may increase pulmonary capillary wedge pressure leading to pulmonary edema